How Do Chemists Describe the Nature of Metallic Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. The bonding in metals is different than both covalent and ionic bonding.

Ionic Vs Covalent Bonds Ionic Vs Covalent Bonds Covalent Bonding Covalent Bonds
Define What is meant by the terms ductility and malleability.

. There are several theories to explain this type of bonding among them the electron sea model is most popular. The electrons are free to move throughout this electron sea. Delocalised electrons are free to move throughout the whole structure.
This forms a sea of electrons that surrounds the metal cations. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Those electrons are the ones that can conduct electricity while they are mobilefree to move.
In these latter two types of bonding interaction the electrons in the bond are localized - that is they either are shared by a pair of atoms or they are associated with one of the. As you can see an electron is freely moving from one atom to another. How do electronegativity values determine the charge distribution in a polar covalent bond.
Metallic bonds are strong and require a great deal of energy to break. Up to 24 cash back Chemists often describe metals as consisting of metal ions floating in a sea of electrons. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability which is gained by forming a full electron shell.
Metallic bonding is a special type of bonding that holds the metals together in metal crystal. The network of metallic bonding. A Ionic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and -.
How do chemists describe the nature of metallic bonding. Describe Describe the nature of metallic bonding in jewelry made from metals. Metallic bonding involves delocacised electrons in a lattice of metal atoms sometimes described as ions in a sea of electrons.
Metallic bond is a term used to describe the collective sharing of a sea of valence electrons between several positively charged metal ions. Metallic bonds result from the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and delocalized electrons. When a metal is molten the metallic bond is still present but the structure is deformed.
This bond is neither covalent nor ionic. These delocalised electrons can move quite freely and can conduct. 1b 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 1c Metallic bonding occurs through delocalized electrons in solid calcium.
A metallic bond is formed when the valence electrons are not associated with a particular atom or ion but exist as a cloud of electrons around the ion centers. The nature of metallic bonding accounts for many of the physical properties of metals such as conductivity and malleability. The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen atoms is very strong.
A sea of electrons that move among metal cations. In contrast covalent and ionic bonds form between two discrete atoms. Up to 24 cash back Name _____ Class _____ Date _____ 3 TEKS Chemistry Lesson 7D Lesson Check 1.
That means that boiling point is actually a way how we can estimate the strength of the metallic bond. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Metallic bonding occurs when you have a metal in the solid or liquid state.
As one metal atom loses an electron and becomes a positively charge ion it immediately accepts one from another to become a neutral atom. Explain Why is the sea of electrons a useful model to describe metallic bonding. Describe metallic bonding and how it contributes to electrical conductivity.
Metallic materials have good electrical and thermal conductivity when compared to materials with covalent or ionic bonding. How does the theory of metallic bonding explain the metallic properties of ductility and malleability. Metals have tendency to give up electrons and none is their to accept it.
Created by Sal Khan. We have an array of atoms bonded to one another that is a network. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound which is formed by the attraction of oppositely charged particles and hence there occurs strong forces of attraction thus forms hard crystalline solid while.
The mutual attraction between all these positive and negative charges bonds them all together - Atom to electron to atom to electron and so forth. Valence electrons of atoms in a pure metal to behave as a sea of electrons. A sea of electrons that move among metal cations.
Electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cationspositive metal ions AND a sea of delocalized electrons mobile electrons responsible for conductivity OR. Apply Theories Apply the theory of metallic. Ionic covalent and metallic.
What type of bond froms when one or more electrons transfer from one atom to another atom changing both atoms into ions. How do chemists describe the nature of metallic bonding. This back and forth losing and gaining of electrons among atoms of the metal allow metals to easily conduct electricity.
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding and is responsible for several characteristic properties of metals such as their shiny lustre their malleability and their conductivities for heat and electricity. How does a covalent bond work. The s and p valence electrons of metals are loosely held.
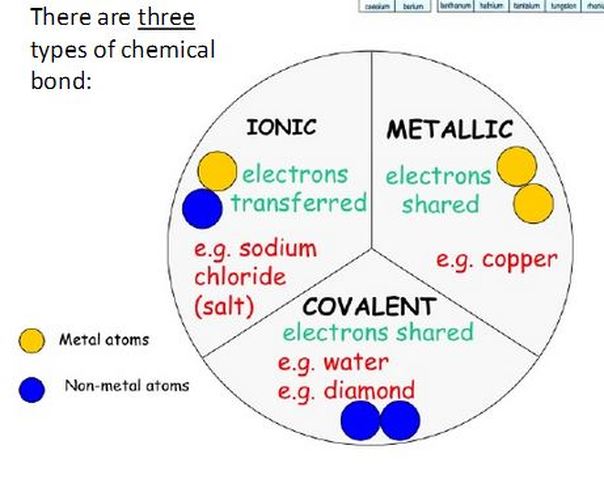
How do chemists describe the nature of metallic bonding. There are three primary types of bonding. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
Is the attraction between the positive ions in a regular lattice and the delocalised electrons. When the metal is heated up to the boiling point the metal bond is broken. In contrast covalent and ionic bonds form between two discrete atoms.
When a metal is subjected to pressure metal cations can slide past one another because electrons insulate them.
2 Bonding And Structure And The Properties Of Matters Thomas Tallis Science

No comments for "How Do Chemists Describe the Nature of Metallic Bonding"
Post a Comment